Introduction:
Stains are an inevitable part of life. Whether it’s spilling coffee on your favourite shirt, ink on your office desk, a stubborn wine stain on the carpet, or a paint spill on a wooden floor, dealing with stains can be frustrating. However, you can conquer even the toughest stains with the correct knowledge, product, and techniques. This comprehensive guide will explore effective stain removal methods for various surfaces and materials, empowering you to keep your belongings spotless and pristine.
Understanding Stains:
Before diving into specific stain removal techniques, it’s crucial to understand the nature of stains. Stains fall into different categories, such as oil-based, water-based, protein-based, or dye-based. Each type requires a different approach to achieve optimal results, and there are different types of stain removers to tackle every kind of stain. We will delve into these categories and provide insights on tackling each one effectively. Some general stain removal tips apply to most stains. From acting quickly and blotting instead of rubbing to testing stain removers on inconspicuous areas, these simple yet crucial tips will help you minimise damage and maximise the chances of successful stain removal.
Stains and marks on clothing are the first stains we think of, but stains can happen on carpets and hard surfaces. Many different things can cause these stains, which fall into the categories of oil, water, protein or dye-based. To remove the stain effectively, you must approach each of them differently.
Note:
It is essential to read the washing instructions for your garment and follow the stain remover’s directions for use, as some stain removers are for specific stains or surfaces and can be harsh and damage certain materials or surfaces. It’s also recommended to first test the stain remover on a small, inconspicuous area to ensure it doesn’t cause any adverse effects or discolouration. Consult with professionals or refer to specific stain removal guides for challenging stains.
Types of stain removal products:
They fall into a few different categories. The three (3) most commonly used are Solvent-action, Oxy-action or Enzyme-action.
Solvent-action
A solvent-action stain remover is a cleaning product designed to remove stubborn stains, including those on hard surfaces. It contains solvents that are effective at dissolving and breaking down marks caused by grease, oil, ink, paint, or adhesive residues.
The solvents used in these stain removers can dissolve or loosen the stain particles, making them easier to remove. Some common solvents used in stain removers include ethanol, isopropyl alcohol, acetone, or other volatile organic compounds.




When using a solvent-action stain remover, you apply the product directly to the stained area and allow it to sit for a specified period to allow the solvent to penetrate and break down the stain. Afterwards, you can use a cloth, sponge, or brush to loosen the stain particles. Finally, rinse or wash the item thoroughly with water or follow the instructions provided by the specific stain remover product.
Oxy-action
An oxy-action stain remover is a cleaning product that uses oxygen-based ingredients to remove stains from various surfaces. These stain removers are typically formulated with hydrogen peroxide (bleaching agent) and other active oxygen-releasing compounds.
The oxygen-based ingredients in oxy-action stain removers break down the chemical bonds of the stain molecules, effectively loosening and lifting the stain from the surface. They are particularly effective at removing organic stains caused by food, beverages, blood, grass, or sweat.




To use an oxy-action stain remover, apply the product directly to the stained area and allow it to penetrate for a certain period. The oxygen-based ingredients will then work to break down the stain. Afterwards, you can rinse the area with water or launder the stained fabric according to the instructions.
Oxy-action stain removers are often available in various forms, including powders, gels, sprays, or pre-soaked wipes. They can be used on many surfaces, including clothing, carpets, upholstery, and hard surfaces like countertops or tile floors.
Enzyme-action
An enzyme-action stain remover is a cleaning product that uses enzymes to break down and remove specific stains. Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions. In the case of stain removers, enzymes are used to target and break down specific types of organic stains, such as those caused by food, blood, grass, or bodily fluids.




Different enzymes
Different enzymes are used in stain removers to target different types of stains. For example, proteases are enzymes that break down proteins and effectively remove protein-based stains like blood or grass. Amylases target starch-based stains, lipases break down lipid or grease stains, and cellulases help remove stains from plant-based fibres like cotton or linen.
Enzyme-action stain removers typically come in liquid or powder forms. To use them, you apply the product directly to the stained area, ensuring it comes into contact with the stain. The enzymes in the stain remover work by breaking down the complex molecules of the stain into smaller, more soluble components, making them easier to remove.
After applying the enzyme-action stain remover, it is usually recommended to let it sit for a certain period, allowing the enzymes to work on the stain. Then, you can wash the fabric or rinse the surface according to the product instructions. The washing or rinsing process helps to flush away the broken-down stain particles, leaving the surface or garment clean.
Enzyme-action stain removers are generally considered safe for use on various fabrics and surfaces. Still, it’s always advisable to follow the instructions provided with the specific product and test on a small, inconspicuous area before applying it to the entire stain. This helps ensure compatibility and avoid any potential damage or discolouration.
Will one stain remover remove all stains?
While some stain removers are designed to be versatile and effective on various types of stains, it is important to note that not all effectively remove every stain. Different stains are composed of different substances, and certain stains may require specific treatment methods or specialised stain removers for optimal results.
For example, a stain remover designed specifically for protein-based stains like blood or grass may not be as effective on grease or oil stains. Similarly, a stain remover formulated for removing ink or dye stains may not work as well on food or beverage stains.
It is recommended to read the instructions for the stain remover before you use it. Many stain removers specify the types of stains they are effective against or provide guidelines for different stain types. Some stain removers may have a broader spectrum of effectiveness, while others are more specialised.
Suppose you are dealing with various types of stains. In that case, you might consider using different stain removers or trying a multi-purpose stain remover that claims to work on multiple stain types. It is good practice to pre-treat specific stains with appropriate stain removers before laundering or cleaning the surface.
Laundry Stain Removers:
These products are formulated to remove many types of stains from clothing and fabrics. Some will be formulated with a combination of active ingredients to help remove a broad range of stains. They come in different forms, such as sprays, sticks, gels, or powders.
Carpet Stain Removers:
Carpet stain removers are designed to tackle carpets, rugs, and upholstery stains. They usually have a combination of active ingredients to help remove a broad range of colours. They come in spray or foam forms and are applied directly to the stain.
Multi-Surface Stain Removers:
These versatile stain removers can be used on many types of surfaces, like countertops, tiles, walls, and floors. They are generally available in spray or liquid form.
Upholstery Stain Removers:
Upholstery stain removers are specifically formulated to remove stains from furniture, including sofas, chairs, and mattresses. These are formulated to be used on many different types of upholstery. They are often available as sprays or foams.
Stain Remover Pens/Sticks/Mini-sprays:
These products are handy for treating stains on the go. The convenient size of the pen, sticks and mini-sprays allows you to carry it and apply the stain remover directly to the affected area as soon as possible.
Rust Stain Removers:
These products are designed to remove rust stains from surfaces such as metal, concrete, or clothing. They often contain acidic compounds that dissolve the rust.
Oil, ink and Grease Stain Removers:
These are solvent-based and designed to tackle oily and greasy stains from fabrics, carpets, and hard surfaces. They usually contain solvents that break down the oil or grease.
Specialised Stain Removers:
There are also stain removers available for specific purposes, such as ink, wine, or pet stain removers, each tailored to address those particular stains. Some will be a dedicated solvent, oxy or enzyme-based stain remover.
When using stain removal products, it’s essential to follow and read carefully the instructions provided by the manufacturer. Washing or rinsing items helps to flush away the broken-down stain particles. Additionally, always test the product on a small, inconspicuous area first to ensure compatibility with the surface or fabric you treat.
What do the symbols on your laundry tags mean
Check out this from the Business Insider.
Interpreting the laundry symbols on your clothing tags can be like walking into a pyramid and trying to read the hieroglyphics. They’re opaque, minimalist, and may have been written by an ancient alien race.
Should you wash your sweater with warm or cold water? Will an ironing or bleaching destroy your khakis? Here, finally, are the answers.f9Check out the graphic below to see what those mysterious symbols actually mean.

How to remove stains:
It is essential with any stain to ACT QUICKLY. The sooner you act, the better your result in removing the stain or mark. Understanding what the stain is made from and which stain remover is best. This diagram from Compound Chemistry helps explain the chemistry of stain removal.
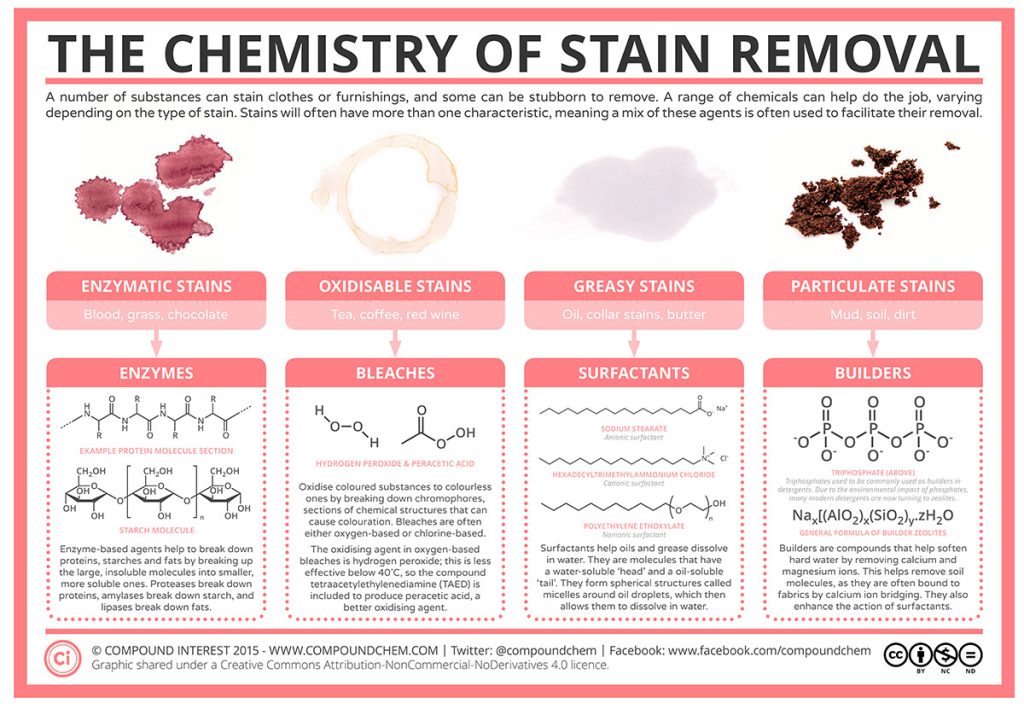
Oil-based stains can be stubborn and challenging to remove. They are caused by substances that contain oils or fats. These stains are typically resistant to water-based cleaning methods because oil and water do not mix. Oil-based stains can come from a variety of sources, including:
- Cooking oils and grease: Splatters and spills of cooking oils or greasy substances in the kitchen can leave behind oil-based stains on surfaces, fabrics, or carpets.
- Motor oil and lubricants: Spills or leaks of oil, lubricants, or other oily automotive fluids can lead to oil-based stains on driveways, garage floors, or clothing.
- Cosmetics and personal care products: Makeup, lotions, hair products, or other personal care items that contain oils can result in oil-based stains on fabrics, carpets, or upholstery.
- Oil-based paints: During painting projects, accidental spills or splatters of oil-based paints can cause oil-based stains on surfaces, fabrics, or clothing.
- Greasy or oily foods: Foods like butter, salad dressings, mayonnaise, or sauces can leave behind oily stains on tablecloths, clothing, or upholstery.
Oil-based stains require specific treatment methods to effectively remove them. Water alone is usually insufficient for removing these stains because oil and water repel each other. Specialised solvents, degreasers, or surfactants are commonly used to break down the oil or grease and lift it from the surface or fabric.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you tackle oil-based stains and marks:
- Act quickly: Treat the stain immediately to prevent it from becoming permanently set.
- Blot the stain: Gently blot the stain with a clean paper towel or cloth to absorb any excess oil. Avoid rubbing the stain, as it may push the oil/stain deeper into the fabric, making it worse and harder to remove.
- Pre-treat stains: Apply a small amount of liquid dish soap or a specialised pre-treatment product directly onto the stain. Gently work the soap into the fabric with your fingers or a soft brush. DO NOT RUB. Let it sit for 10 to 15 minutes to allow the soap to penetrate the stain.
- Launder the garment: Wash the garment following the care instructions on the label as soon as possible. Use the warmest water recommended for the fabric type. Check the label to ensure you don’t use too warm/hot water for the fabric.
- Check for stain removal: After laundering, inspect the stained area to see if the oil stain has been removed. If the stain persists, do not put the garment in the dryer, as the heat can make the stain permanent. Repeat the pre-treatment process and rewash the garment.
- Consider alternative methods: If the stain persists after regular laundering, you can try other methods, such as using a solvent-based stain remover or applying a paste of baking soda and water. Let it sit for a few hours before rewashing the garment.
- Dry the garment: Once the stain is successfully removed, air-dry the garment or follow the drying instructions on the label.
Water-based stains are generally easier to remove than oil-based ones as they are caused by substances that are soluble in water or have high water content. These stains are usually easier to remove than oil-based ones because water-based stains can be effectively diluted and rinsed away with water. Some common sources of water-based stains include:
- Beverages: Spills of water, coffee, tea, juice, soda, or other drinks can leave behind water-based stains on fabrics, carpets, or surfaces.
- Food stains: Foods that contain water or have a high water content, such as fruits, vegetables, sauces, or soups, can result in water-based stains on clothing, tablecloths, or upholstery.
- Water-soluble paints or dyes: Certain paints or dyes, mainly watercolour paints, fabric dyes, or water-based inks, can leave behind water-based stains on various surfaces.
- Ink or marker stains: Water-based ink or marker stains, commonly found in pens, markers, or fountain pens, are soluble in water and can result in water-based stains on paper, clothing, or other surfaces.
- Cleaning products: Some cleaning products, such as liquid detergents, soaps, or cleaning sprays, are water-based and can leave behind water-based stains if not adequately rinsed or removed.
Water-based stains can often be effectively treated with water and mild detergents or stain removers formulated for water-based stains. Blotting or rinsing the stained area with water can help dilute and remove the stain. However, it’s important to follow specific instructions for the stain removal product or consult professional advice for stubborn stains or delicate garments.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you remove water-based stains from clothes:
- Act quickly: Attend to the stain immediately to prevent it from setting and becoming permanent.
- Blot the stain: Do not rub. Using a paper towel or a clean cloth gently blot the stained area, absorbing as much liquid as possible. Avoid rubbing, as it can spread the stain.
- Rinse with cold water: Hold the stained area under cold running water, allowing the water to flow through the fabric from the backside. This helps flush out the stain.
- Apply stain remover: Depending on the type of stain, you can use a liquid laundry detergent, a stain remover, or a mixture of water and vinegar. Apply a small amount of the chosen solution directly to the stain and using your fingers or a soft brush gently work it into the fabric.
- Soak the garment: If the stain persists, you can soak the garment in a solution of water and detergent or an enzymatic stain remover. Check the label care instructions for the recommended soaking time.
- Launder the garment: After pre-treating or soaking, wash the garment following the care instructions on the label. Use the warmest water temperature that is safe for the fabric.
- Check for stain removal: Once the garment is washed, inspect the stained area to see if the water-based stain has been removed. If the stain is still visible, do not use a dryer to dry the garment, as the heat can make the stain permanent. Repeat the pre-treatment or soaking process and rewash the garment.
Air-dry or tumble-dry: Once the stain is successfully removed, either air-dry the garment or follow the drying instructions on the label.
Protein-based stains, such as blood, sweat, or food, can be more challenging to remove from clothes. Delicate or valuable items may require professional cleaning. These are caused by substances that contain proteins or are derived from organic materials like animals or plants. Removing them can be challenging because proteins can bind tightly to fabrics and surfaces. Common sources of protein-based stains include:
- Blood: Bloodstains, whether from minor cuts, nosebleeds, or accidents, contain proteins that can leave behind stubborn stains on fabrics, carpets, or upholstery.
- Grass: Grass stains, often encountered on clothing or sports equipment, are protein-based stains from chlorophyll and other proteins in the grass.
- Eggs: Spills or splatters of raw or cooked eggs can lead to protein-based stains that are particularly difficult to remove due to the coagulation of proteins during cooking.
- Dairy products: Milk, yoghurt, cheese, or ice cream can leave behind protein-based stains that can become more challenging to remove if not addressed promptly.
- Bodily fluids: Perspiration, saliva, or other bodily fluids contain proteins that can result in protein-based stains on clothing, bedding, or upholstery.
Protein-based stains require specific treatment methods to effectively remove them. Enzyme-based stain removers are often recommended for breaking down the proteins in these stains. The enzymes, such as proteases, work to break down the protein molecules and help lift the stain from the fabric or surface.
When treating protein-based stains, it’s important to address them as soon as possible to prevent the proteins from setting and bonding more strongly to the material. Following the instructions provided by stain removal products, pre-soaking in enzyme-based solutions, or seeking professional advice can assist in effectively removing protein-based stains.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you tackle protein-based stains effectively:
- Act quickly: Treat the stain immediately to prevent it from setting into the fabric. The longer the stain sits, the more difficult it becomes to remove.
- Rinse with cold water: Hold the stained area under cold running water to flush out as much protein as possible. Avoid using hot water as stains can become permanent.
- Pre-treat the stain: Apply directly onto the stain a small amount of liquid detergent or enzyme-based stain remover. Gently work the solution into the fabric using your fingers or a soft brush. Let it sit for 10 to 15 minutes to let the detergent or stain remover penetrate the stain.
- Launder the garment: Wash the garment following the care instructions on the label. Use the warmest water recommended for the fabric, but again, avoid using hot water. Check the label to ensure that warm water is safe for the garment.
- Check for stain removal: After laundering, check the stained area to see if the protein-based stain has been removed. If the stain is still visible, do not use a dryer to dry the garment, as the heat can make the stain permanent. Repeat the pre-treatment process and rewash the garment.
- Consider alternative methods: If the stain persists after regular laundering, use hydrogen peroxide (for white or colorfast fabrics) or apply a baking soda and water paste to the stain. Be sure to test these methods on a small, inconspicuous area of the garment before applying them to the stained area.
Air-dry or tumble-dry: Once the stain is successfully removed, either air-dry the garment or follow the drying instructions on the label.
Dye-based stains can be pretty challenging to remove from clothes, especially if the dye has penetrated deep into the fabric fibres. Be aware that some dyes are more resistant and may be impossible to remove altogether. These stains are caused by substances that contain coloured dyes or pigments. These stains occur when the dye molecules transfer from the source material onto another surface, resulting in discolouration. Dye-based stains can be quite persistent and challenging to remove, especially if the dye is deeply absorbed or chemically bonded to the material. Some common sources of dye-based stains include:
- Clothing dyes: Dye transfer can occur when garments with unstable or excess dyes come into contact with other fabrics during washing or wearing. This can result in dye-based stains on clothes.
- Ink: Ink stains from pens, markers, or printers can be dye-based stains. The composition of the ink can vary, but many inks contain dyes that can leave behind stubborn stains.
- Hair dye: Accidental spills or contact with hair dye can lead to dye-based stains on various surfaces, including clothing, countertops, or bathroom fixtures.
- Food colouring: Foods or beverages with artificial colouring, such as brightly coloured drinks or lollies, can leave behind dye-based stains if they come into contact with fabrics or other surfaces.
Removing dye-based stains can be challenging, often requiring specific techniques and products. The approach to stain removal may depend on the type of dye, the material it has stained, and the severity of the stain.
It’s important to note that not all dye-based stains can be removed entirely, especially if the dye has permanently altered the colour of the material. Prevention is often the best approach, such as following garment care instructions, separating laundry by colour, or using protective measures when working with dyes.
However, here are some steps you can take to try and remove dye-based stains:
- Act quickly: If you notice a dye-based stain, try to treat it as soon as possible. The longer the stain sets, the more difficult it becomes to remove.
- Rinse with cold water: Immediately flush the stained area with cold water to remove as much of the dye as possible. Hold the fabric under running water, allowing it to flow through the backside of the stain.
- Apply stain remover or detergent: Apply directly onto the stain a stain remover or liquid laundry detergent. Gently work it into the fabric with your fingers or a soft brush. Let it sit for a few minutes to allow the stain remover or detergent to penetrate the fibres.
- Soak the garment: If the stain persists, try soaking the garment in a solution of water and oxygen-based stain remover or bleach. Follow the instructions on the product and soak the garment for the recommended time. Not all fabrics can tolerate bleach, so check the care label before using this method.
- Launder the garment: After pre-treating or soaking, wash the garment as usual, following the care instructions on the label. Use the warmest water recommended for the fabric unless otherwise specified.
- Check for stain removal: Once the garment is washed, inspect the stained area to see if the dye-based stain has been removed. If the stain is still visible, do not use a dryer to dry the garment, as the heat can make the stain permanent. Repeat the pre-treatment or soaking process and rewash the garment.
- Seek professional help: If the dye-based stain persists after repeated attempts, it may be best to seek professional dry-cleaning services. Professional cleaners have specialised stain removal techniques and products that can be effective against stubborn stains.
Remember, it is essential to read the washing instructions for your garment and follow the stain remover’s directions for use, as some stain removers are for specific stains or surfaces and can be harsh and damage certain materials or surfaces. It’s also recommended to first test the stain remover on a small, inconspicuous area to ensure it doesn’t cause any adverse effects or discolouration. Consult with professionals or refer to specific stain removal guides for challenging stains.
Summary:
Stains don’t have to be permanent. With the knowledge and techniques shared in this comprehensive stain removal guide, you can confidently tackle various stains. You’ll have the tools and strategies to maintain a spotless environment from clothing to carpets, hard surfaces to leather. So, embrace a stain-free life and say goodbye to those stubborn spots that once plagued your belongings.
How can Magic help?
Visit our product pages to learn more, see before and after photos and read customer reviews.
- Magic Stain Remover Solvent-action – Our Australian Made & Owned Magic Solvent-Power Stain Remover is formulated to start working immediately to help prevent stains from becoming permanently set. Ideal for stains and marks made by: coffee, wine, food, blood, sauce and more. It can also be used on carpets, furniture and walls.
- Bleach-free
- Great on Everyday Stains
- Hard & Soft Surfaces
- Septic and Grey Water Safe
- Bottle Made from 100% Recycled Plastic
- Magic Mini Stain Remover Twin Pack – Magic Mini Stain Remover Twin Pack provides two (2) convenient on-the-go stain removers, no bigger than a pen. Formulated to start working immediately to help prevent stains from becoming permanently set.
- Magic Solvent Stain Remover Mini Spray is ideal for grease, lipstick and paint stains
- Magic Oxy-Power Stain Remover Pen is ideal for coffee, wine, food, blood, and sauce stains
- Both are Bleach-free, Great on Everyday Stains, Work in Cold or Hot Washes and are Septic and Grey Water Safe
